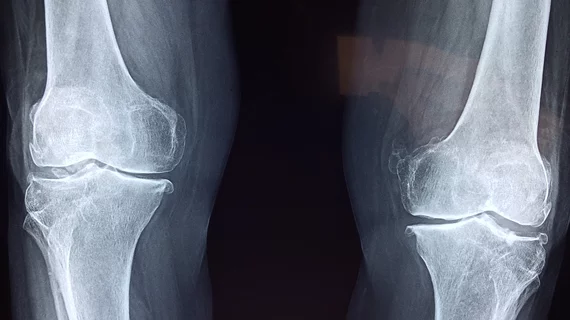
FDA clears artificial intelligence algorithm for diagnosing osteoarthritis on knee X-rays
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has OK’d a new artificial intelligence algorithm for diagnosing osteoarthritis using X-rays of the knee.
Creator Radiobotics said this is its first 510(k) clearance, following certification in Europe earlier this year. RBknee analyzes radiographs of the joint, helping radiologists and orthopedists identify common imaging findings tied to the condition, including osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis and joint space narrowing.
“As the global population ages, the demand for healthcare services is only going to accelerate, and with the first product FDA cleared, we’re now ready for the next step in our contribution to the digitization of the health industry,” Ayse McCracken, chair of startup’s board of directors, said in statement.
Radiobotics is based in Copenhagen, Denmark, and was first founded in 2017. The firm noted that 10% of the world’s population over age 60 have joint problems related to arthritis, a number expected to swell in the coming years. Those involved said the software was cleared following testing and clinical validation demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity.