Pulmonary embolism
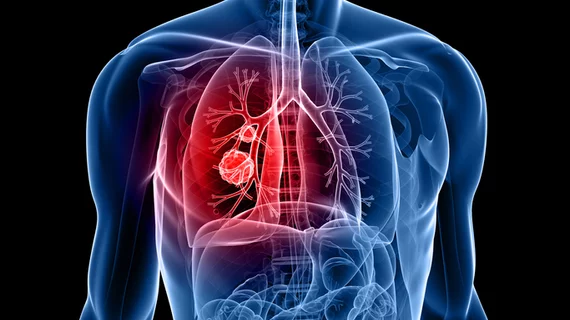
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the third leading cardiovascular cause of death after heart attacks and stroke. PE is caused by blood clots in the pulmonary arteries. These are often caused by clots from the venous system, including thrombus from trauma, surgery or deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Treatment has traditionally been systemic use of thrombolytic drugs to dissolve the clot. But in cases there is a massive, life-threatening PE, or chronic clot burden that have remained in a vessel for an extended period of time, mechanical thrombectomy and ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis (USCDT) is being used as more targeted and aggressive treatments.